HISTORICAL THINKING CONCEPTS
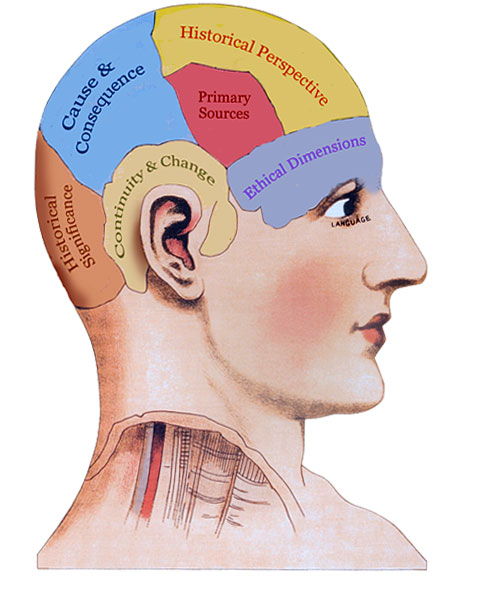 The Historical Thinking Project works with six distinct but closely interrelated historical thinking concepts. To think historically, students need to be able to:
The Historical Thinking Project works with six distinct but closely interrelated historical thinking concepts. To think historically, students need to be able to:
- Establish historical significance
- Use primary source evidence
- Identify continuity and change
- Analyze cause and consequence
- Take historical perspectives, and
- Understand the ethical dimension of historical interpretations.
Taken together, these concepts tie “historical thinking” to competencies in “historical literacy.” In this case, “historical literacy” means gaining a deep understanding of historical events and processes through active engagement with historical texts.
Historically literate citizens can assess the legitimacy of claims that there was no Holocaust, that slavery wasn't so bad for African-Americans, that aboriginal rights have a historical basis, and that the Russian experience in Afghanistan serves as a warning to the Canadian mission there. They have thoughtful ways to tackle these debates. They can interrogate historical sources. They know that a historical film can look "realistic" without being accurate. They understand the value of a footnote.
In short, they can detect the differences, as Margaret MacMillan's book title reads, between the uses and abuses of history. “Historical thinking” only becomes possible in relation to substantive content. These concepts are not abstract “skills.” Rather, they provide the structure that shapes the practice of history.

